Why Is Standard Deviation Important in Quality Control?
In quality control, precision and consistency are key. Businesses and industries depend on maintaining high-quality standards to meet customer expectations and comply with regulations. One crucial tool in this process is standard deviation. This statistical measure is vital in determining how much variation exists within a set of data, which is essential for maintaining control over product quality.
Understanding why standard deviation is so important in quality control helps ensure that products are consistently produced within acceptable limits. Let’s dive into why this concept is fundamental for any business focused on delivering quality.
Ensuring Consistency and Reducing Variability
In manufacturing and production, consistency is critical. The goal is to produce items that meet predefined standards every time. Standard deviation measures the amount of variation in the production process. By analyzing how far the data deviates from the average (or mean), manufacturers can detect if there’s too much variation, which often indicates a problem in the process.
When the standard deviation is low, it means that the data points (such as product measurements, weights, or dimensions) are clustered closely around the mean, indicating a high level of consistency. However, a high standard deviation suggests that the process may be producing products that deviate significantly from the desired standard, leading to defects or out-of-spec items. By monitoring standard deviation, businesses can identify and correct issues early, reducing waste and ensuring quality.
Setting Acceptable Quality Levels
In quality control, companies often establish Acceptable Quality Levels (AQL)—a statistical threshold that determines the maximum number of defective units that are acceptable in a given batch. Standard deviation plays a crucial role in setting these levels. It helps businesses decide what level of variability is acceptable before products are considered defective.
For example, if a company produces bolts with a specified diameter, they may allow a certain small variation in size, but if the standard deviation grows too large, it may indicate that too many bolts are out of spec. In this way, standard deviation serves as a critical benchmark in ensuring that products meet the company’s quality standards, and it enables businesses to maintain consistency while keeping the number of defective products to a minimum.
Enhancing Process Control with Six Sigma
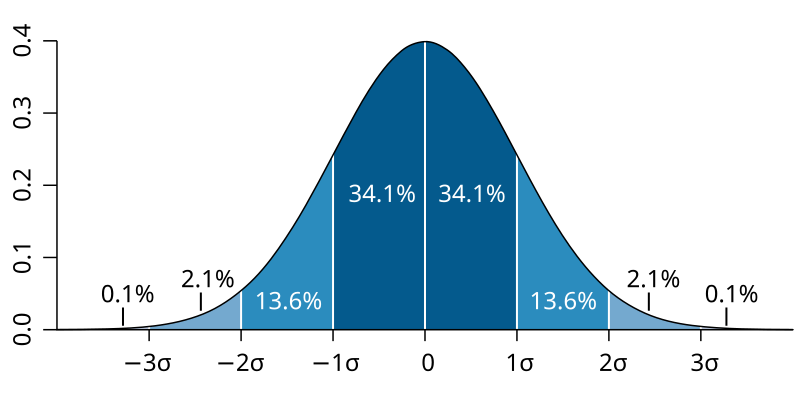
Six Sigma, a well-known quality control methodology, heavily relies on standard deviation. The goal of Six Sigma is to reduce defects to near perfection—no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. This methodology aims for six standard deviations between the mean of the process and the nearest specification limit, which translates to minimal variation and nearly flawless products.
By closely monitoring standard deviation, companies using Six Sigma can assess how well their production processes are performing. If the standard deviation is large, it means the process is producing too much variation, leading to defects and failures. Reducing the standard deviation in the process directly aligns with achieving Six Sigma’s goal of near-perfect quality, allowing businesses to improve both efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Identifying Process Improvements
Standard deviation doesn’t just measure variation—it also highlights opportunities for process improvement. If a company notices that the standard deviation in a particular production line is increasing, it indicates that something in the process may be going wrong. This could be due to wear and tear on machinery, operator error, or a problem with the raw materials.
By using standard deviation as a diagnostic tool, businesses can pinpoint the source of the problem and take corrective action. For instance, if a packaging machine is consistently overfilling or underfilling products, increasing variation in the product weight, the company can service the machine or recalibrate it to bring it back within the acceptable range. In this way, standard deviation helps companies stay proactive in maintaining quality and efficiency in their operations.
Minimizing Defects and Waste
One of the biggest challenges in manufacturing is reducing defects and waste. When variation in the production process is too high, it can lead to products that don’t meet specifications, resulting in wasted materials and labor. Standard deviation provides an early warning signal that the process is moving out of control.
By monitoring the standard deviation, quality control teams can quickly intervene when they see that variability is increasing beyond acceptable limits. This minimizes the number of defective products that reach customers or need to be scrapped. Reducing waste not only saves money but also helps companies meet sustainability goals by using resources more efficiently.
Improving Customer Satisfaction
Customers expect high-quality products that meet their needs every time. When variability in the production process leads to defects, it can damage customer trust and satisfaction. By using standard deviation to monitor and control variation in the production process, companies can produce more consistent, high-quality products.
Reducing variation means fewer defective products, which leads to fewer customer complaints, returns, and refunds. Standard deviation helps companies meet customer expectations for consistency and reliability, which in turn enhances brand loyalty and satisfaction.
Supporting Predictive Maintenance
Another important role of standard deviation in quality control is supporting predictive maintenance. Machines and equipment naturally wear down over time, leading to more variation in the production process. By monitoring the standard deviation of product measurements or other key metrics, companies can detect when a machine is starting to produce too much variation, indicating that maintenance is needed.
For example, if the standard deviation of a machine’s output begins to increase over time, it may signal that the machine needs calibration, repair, or replacement. This proactive approach reduces unexpected downtime, prevents costly breakdowns, and ensures that production continues smoothly with minimal disruption.
Using Control Charts for Continuous Monitoring
In quality control, control charts are used to monitor the stability of processes over time. These charts plot the mean and standard deviation of key metrics, helping companies track the performance of their production processes in real-time. A control chart will have upper and lower control limits, which are typically set at three standard deviations from the mean.
If data points fall outside these limits, it indicates that the process is no longer under control and corrective action needs to be taken. This continuous monitoring helps companies maintain tight control over product quality, ensuring that any deviations from the standard are quickly detected and addressed. Standard deviation is central to the construction of these control charts, making it an indispensable tool for ongoing quality management.
Promoting Data-Driven Decisions
One of the biggest advantages of using standard deviation in quality control is that it promotes data-driven decision-making. Instead of relying on intuition or guesswork, companies can base their quality control decisions on hard data. Standard deviation provides a clear, quantifiable measure of variation, allowing quality control teams to make informed decisions about when and how to intervene in the production process.
Data-driven decisions lead to better outcomes because they are based on evidence, not assumptions. By relying on standard deviation as a key metric, companies can ensure that their quality control efforts are targeted, effective, and efficient.
Conclusion: A Key Tool for Consistent Quality
Standard deviation is an essential component of quality control because it allows businesses to measure, monitor, and manage variation in their processes. By understanding and applying standard deviation, companies can maintain consistency, reduce defects, and improve overall product quality.
From setting acceptable quality levels to supporting predictive maintenance, standard deviation plays a crucial role in ensuring that production processes remain under control. By using this powerful statistical tool, businesses can not only reduce waste and defects but also enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. In the world of quality control, standard deviation truly makes the difference between mediocrity and excellence.
click here to visit website













Post Comment