What Are the Long-Term Effects of Giardiasis?
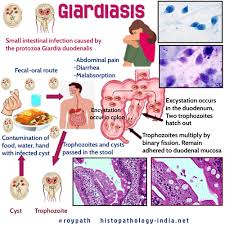
Giardiasis, caused by the protozoan parasite Giardia lamblia (also known as Giardia intestinalis or Giardia duodenalis), is a common intestinal infection. It is typically contracted through contaminated water, food, or direct contact with infected individuals. While the acute symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal cramps, bloating, and fatigue are often the most noticeable, the long-term effects of giardiasis can be significant and varied. This article explores these long-term consequences and emphasizes the role of treatments such as nitazoxanide 500mg in managing the infection.
Overview of Acute Giardiasis
The initial infection usually results in gastrointestinal symptoms that appear 1 to 3 weeks after exposure. These symptoms can persist for several days to weeks. While many individuals recover spontaneously, others experience persistent or recurrent symptoms. Giardiasis can progress to chronic or long-term illness, especially if left untreated or inadequately managed.
Long-Term Effects of Giardiasis
For some individuals, giardiasis does not end with the resolution of acute symptoms. The infection can lead to a range of long-term health issues, which are often underestimated. These include gastrointestinal complications, nutritional deficiencies, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), fatigue, and other systemic effects.
1. Chronic Gastrointestinal Issues
Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms are one of the most common long-term effects of giardiasis. Even after the parasite is eradicated, some individuals continue to experience abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea. These symptoms may be due to ongoing inflammation or damage to the intestinal lining caused by the parasite during the acute phase of the infection.
2. Malabsorption and Nutritional Deficiencies
Giardiasis can cause damage to the small intestine, leading to malabsorption of essential nutrients. This is particularly concerning in children, as it can impair growth and development. Common deficiencies associated with giardiasis include:
- Vitamin A and B12 deficiencies: These can result from impaired absorption in the small intestine.
- Iron deficiency and anemia: Chronic diarrhea can lead to significant nutrient loss, contributing to anemia.
- Protein-energy malnutrition: Prolonged malabsorption may result in weight loss and reduced muscle mass.
3. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Post-infectious IBS is a recognized consequence of giardiasis. Studies have shown that up to 40% of individuals who recover from giardiasis develop IBS-like symptoms, including altered bowel habits, abdominal pain, and bloating. These symptoms can persist for years and significantly impact the quality of life.
4. Fatigue and Psychological Effects
Chronic fatigue and mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety, are often reported by individuals with a history of giardiasis. The exact mechanisms are unclear but may involve chronic inflammation, immune system dysregulation, or the psychological burden of living with a chronic illness.
5. Long-Term Impacts on Children
For children, the long-term effects of giardiasis can be particularly severe. Chronic infections can lead to stunted growth, cognitive impairments, and poor academic performance due to malnutrition and recurrent illnesses. These impacts are especially pronounced in resource-limited settings where access to healthcare is limited.
The Role of Nitazoxanide 500mg in Giardiasis Treatment
Nitazoxanide 500mg has emerged as an effective treatment for giardiasis, particularly in cases where other treatments, such as metronidazole or tinidazole, have failed or are contraindicated. This broad-spectrum antiparasitic and antiviral agent works by interfering with the energy metabolism of Giardia lamblia, leading to the parasite’s death.
Advantages of Nitazoxanide
Efficacy: Nitazoxanide has shown high cure rates in both adults and children.
Safety Profile: It is generally well-tolerated, with fewer side effects compared to metronidazole, such as the absence of metallic taste and disulfiram-like reactions with alcohol.
Short Treatment Course: Typically administered over 3 days, the regimen is convenient and promotes adherence.
Dosage and Administration
The standard dosage for adults is nitazoxanide 500mg taken orally twice daily with food for 3 days. Pediatric dosing varies based on age and weight, emphasizing the importance of consulting a healthcare provider for appropriate guidance.
Preventing Long-Term Effects
The best way to prevent the long-term consequences of giardiasis is prompt and effective treatment. Nitazoxanide 500mg is a key option in this regard, but additional measures are necessary to ensure full recovery and prevent reinfection:
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment: Seeking medical attention promptly when symptoms of giardiasis occur can reduce the risk of chronic complications.
- Nutritional Support: Addressing malnutrition through dietary supplementation can mitigate the impacts of nutrient deficiencies.
- Hygiene and Sanitation: Practicing good hygiene, such as handwashing and using safe drinking water, can prevent initial infection and reinfection.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider can ensure the complete resolution of the infection and monitor for any long-term effects.
Conclusion
While giardiasis is often considered an acute illness, its long-term effects can significantly impact an individual’s health and well-being. Chronic gastrointestinal issues, malabsorption, IBS, fatigue, and developmental impacts in children are among the key concerns. Treatment with nitazoxanide 500mg offers an effective solution to manage and eradicate the infection, reducing the risk of these complications.
However, a comprehensive approach that includes timely diagnosis, nutritional support, and preventive measures is essential to address the full spectrum of challenges posed by this infection.
By recognizing and addressing the potential long-term effects of giardiasis, individuals and healthcare providers can work together to ensure better health outcomes and an improved quality of life for those affected by this parasitic infection.












Post Comment