The Role of Temperature Control in Pharmaceutical Storage
Pharmaceutical products, including medicines, vaccines, and supplements, are highly sensitive to environmental conditions, especially temperature. Proper storage is essential to maintain their efficacy, quality, and safety. Temperature control plays a pivotal role in ensuring that these products remain effective from production to consumption. In healthcare, supplements, and medical warehouses, maintaining the right temperature is critical to prevent degradation, contamination, or spoilage of pharmaceutical products.
Importance of Temperature Control in Pharmaceutical Storage
Pharmaceutical products are designed to treat or prevent diseases. Their chemical composition is often delicate, making them susceptible to temperature fluctuations. If stored incorrectly, these products can lose their potency, putting patients’ health at risk. Maintaining optimal temperatures in healthcare, supplements, and medical warehouses ensures that the products remain within their specified temperature range, preserving their therapeutic properties.
Protecting Product Efficacy
One of the most significant reasons for strict temperature control is to ensure the efficacy of pharmaceutical products. Medications, vaccines, and supplements can degrade if exposed to temperatures outside their recommended range. For instance, insulin and certain vaccines must be stored at a specific temperature (typically between 2°C and 8°C) to maintain their potency. Deviation from this range can render the products useless or even harmful.
Reducing Health Risks
Temperature control in a healthcare warehouse is not just about preserving the efficacy of products; it’s also about patient safety. Improperly stored medications can result in ineffective treatments, leading to adverse health outcomes. In some cases, such as with vaccines, temperature variations can cause irreversible damage to the product, making it unsafe for use. By maintaining strict temperature conditions, healthcare facilities and warehouses can ensure that products administered to patients are safe and effective.
Meeting Regulatory Standards
Pharmaceutical storage is heavily regulated to protect public health. Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other local authorities have set stringent guidelines for the storage of pharmaceuticals. These guidelines specify temperature ranges for various products and mandate the use of reliable monitoring systems in healthcare and medical warehouses. Failing to comply with these regulations can lead to penalties, product recalls, and reputational damage.
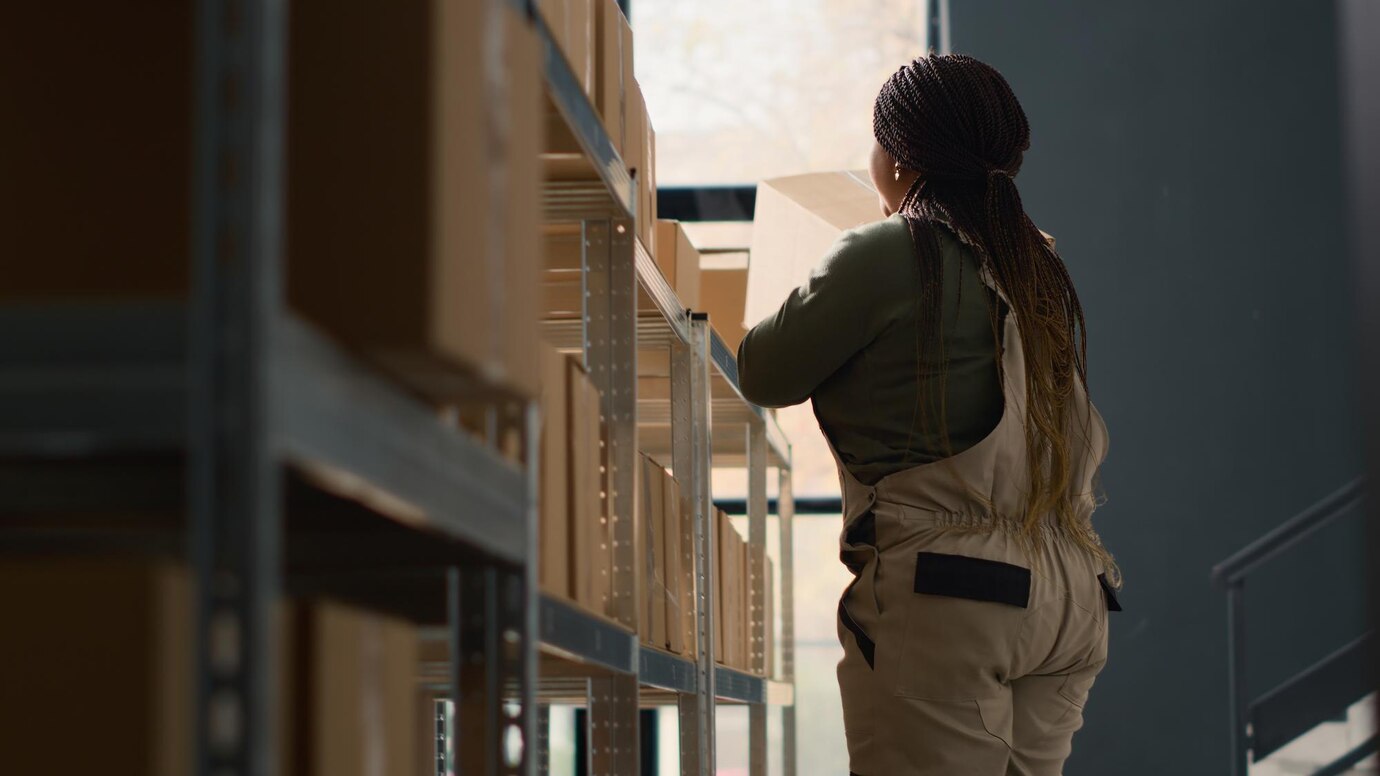
Temperature Control Requirements in Healthcare Warehouses
Healthcare warehouses play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical supply chain. They store large volumes of medications, vaccines, and supplements before they are distributed to hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies. To maintain the integrity of these products, healthcare warehouses must adhere to strict temperature control protocols.
Cold Chain Storage
Certain pharmaceuticals, particularly vaccines and biologics, require cold chain storage. This means that they must be kept at a consistently low temperature throughout the supply chain. Healthcare warehouses must have specialized refrigeration systems and backup generators to ensure that temperature-sensitive products are never exposed to extreme conditions. A well-maintained cold chain ensures that these critical medications remain effective until they reach the patient.
Temperature Monitoring Systems
In a healthcare warehouse, continuous temperature monitoring is essential to prevent product degradation. Automated temperature control systems are commonly used to track and maintain the optimal temperature range. These systems alert warehouse staff if the temperature exceeds or drops below the recommended range, allowing for prompt corrective action. Advanced monitoring systems also generate detailed reports, which are required for regulatory compliance and audits.
Environmental Control for Sensitive Products
Some pharmaceutical products, such as biologics and specialty drugs, are highly sensitive to environmental conditions beyond just temperature. Humidity and light exposure can also affect the stability of these products. Healthcare warehouses must implement environmental controls that include humidity regulation and proper lighting to ensure the safety and efficacy of these sensitive items.
Temperature Control in Supplements Warehouses
Supplements, while not always as sensitive as pharmaceutical drugs, still require proper storage conditions to ensure their quality and safety. Supplements warehouse must implement temperature control measures similar to those used in healthcare warehouses.
Preserving Active Ingredients
Supplements contain active ingredients, such as vitamins, minerals, and herbal extracts, that can degrade when exposed to high temperatures. For instance, Vitamin C and probiotics are particularly vulnerable to heat, losing their potency when stored improperly. Supplements warehouses must maintain a controlled temperature environment to prevent the degradation of these active ingredients, ensuring that consumers receive the full benefit of the products.
Preventing Spoilage of Perishable Supplements
Some supplements, such as fish oil and other omega-3 products, are perishable and can spoil if not stored at the correct temperature. High temperatures can cause these supplements to become rancid, making them unsafe for consumption. Supplements warehouse must be equipped with proper refrigeration and cooling systems to store perishable items and extend their shelf life.
Maintaining Shelf Stability
Supplements often have a long shelf life, but only if stored correctly. Temperature fluctuations can reduce the shelf stability of these products, leading to quality issues before their expiration date. A supplements warehouse must implement effective temperature control measures to maintain the shelf life and overall quality of the products.
Best Practices for Temperature Control in Medical Warehouses
Medical warehouse store a wide range of products, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, medical devices, and vaccines. Each of these products may have different storage requirements, making temperature control a complex but essential task.
Zoning for Different Temperature Requirements
One of the best practices in medical warehouses is zoning, which involves dividing the warehouse into different areas with specific temperature ranges. This allows for the storage of products with varying temperature requirements in the same facility. For instance, a medical warehouse may have a refrigerated zone for vaccines and temperature-sensitive drugs, as well as a controlled room temperature (CRT) zone for products that need to be stored at ambient temperatures.
Backup Power Solutions
Medical warehouses must be prepared for any situation that could compromise temperature control, such as power outages. Backup power solutions, including generators and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, are critical for maintaining the necessary temperature in the event of a power failure. Without these systems, the risk of temperature excursions increases, leading to potential product loss.
Regular Equipment Maintenance
The refrigeration and cooling systems in a medical warehouse must be regularly maintained to ensure that they are functioning properly. Regular maintenance checks help identify any issues that could lead to temperature fluctuations, such as faulty compressors or inadequate insulation. By keeping the equipment in optimal condition, medical warehouses can minimize the risk of product spoilage or degradation.
Training for Warehouse Staff
Even with advanced temperature monitoring systems in place, human oversight is still essential. Medical warehouse staff must be trained to understand the importance of temperature control and how to respond to temperature excursions. Proper training ensures that staff can act quickly to rectify any issues, preventing product loss and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Conclusion
Temperature control is a critical factor in the pharmaceutical storage process, ensuring that medications, vaccines, and supplements maintain their efficacy, quality, and safety. Healthcare, supplements, and medical warehouses must adhere to strict temperature control protocols to protect the integrity of these products. By implementing proper temperature monitoring systems, environmental controls, and staff training, warehouses can ensure that pharmaceutical products are stored under the optimal conditions, safeguarding public health and meeting regulatory requirements.
You might like to read: How to Choose the Right Spotlight for Your Outdoor Space in Qatar












Post Comment