The Role of Food and Water in Amebiasis Infection
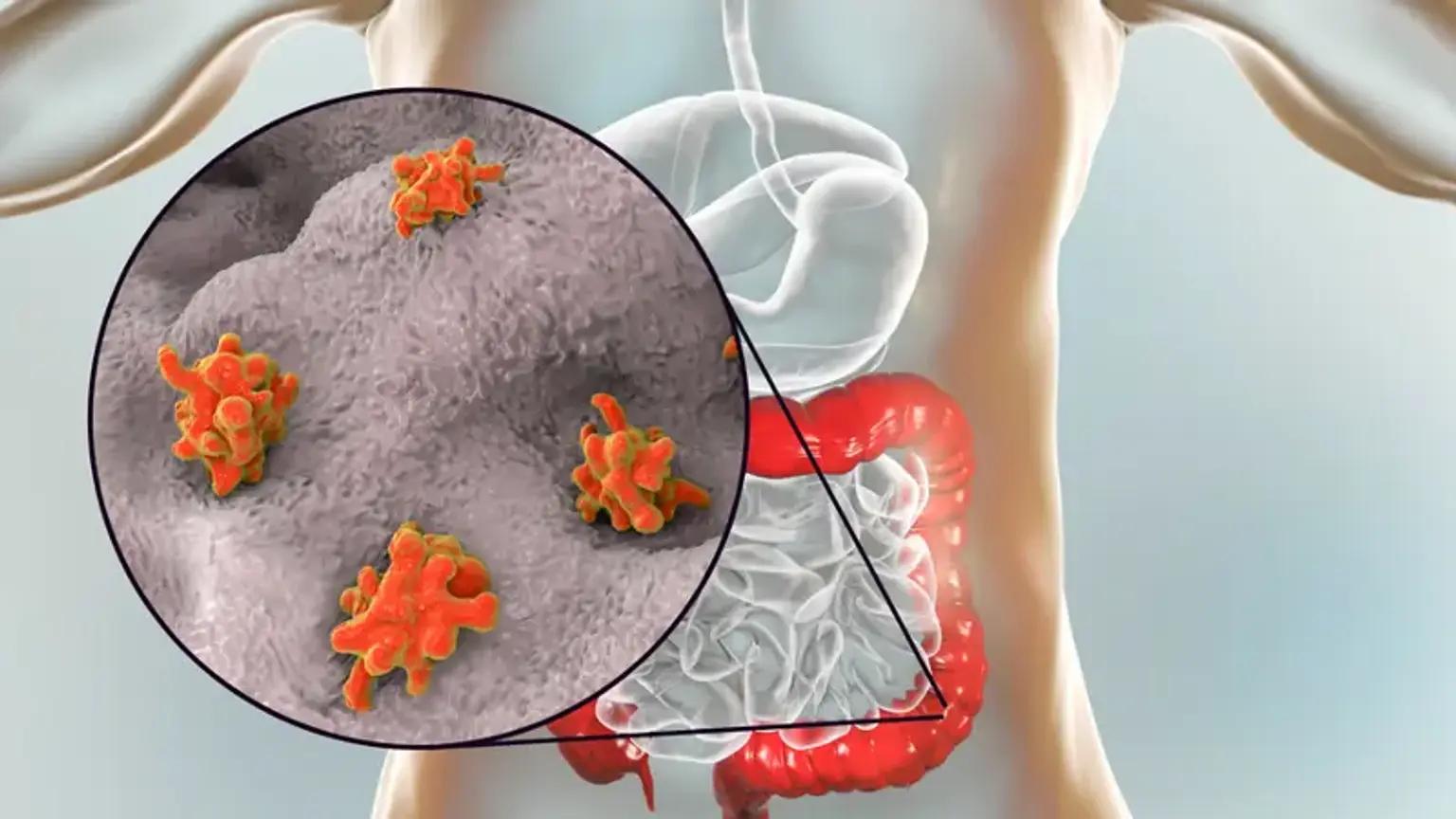
Amebiasis is an intestinal infection caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. It primarily spreads through contaminated food or water and can result in symptoms ranging from mild diarrhea to severe abdominal pain and liver abscesses. The disease is prevalent in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene, but travelers and residents in such regions can take proactive steps to prevent infection. In this article, we’ll explore various prevention strategies and discuss the role of medications, including nizonide, in managing the condition.
Understanding Amebiasis
Amebiasis occurs when Entamoeba histolytica cysts enter the human body through ingestion. Once inside, the cysts transform into trophozoites, which multiply and invade the intestinal lining. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including
- Abdominal cramps
- Diarrhea (sometimes bloody)
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
Severe cases can involve liver abscesses or other organ complications. Early detection and proper management are crucial to avoid these outcomes.
Tips for Preventing Amebiasis
Preventing amebiasis largely involves maintaining proper hygiene, ensuring safe food and water consumption, and being vigilant in areas with poor sanitation. Here are some practical steps to reduce the risk of infection:
1. Practice Good Hygiene
Wash Your Hands
Regular handwashing with soap and water is one of the most effective ways to prevent amebiasis. Pay special attention to washing hands before eating, preparing food, and after using the restroom.
Avoid Touching Your Face
Minimize touching your mouth, nose, and eyes, especially if you’ve been in environments where contamination is possible.
2. Ensure Safe Drinking Water
Drink Boiled or Bottled Water
In areas where water quality is uncertain, always opt for boiled, filtered, or bottled water. Avoid ice cubes made from tap water.
Use Water Purification Tablets
These tablets can be effective in neutralizing parasites in water when boiling isn’t feasible.
3. Be Cautious with Food
Eat Cooked Foods: Thoroughly cooked food is less likely to harbor Entamoeba histolytica. Avoid raw or undercooked meats, seafood, and unpeeled fruits and vegetables.
Peel Fruits and Vegetables
If raw fruits and vegetables are unavoidable, peel them yourself to ensure cleanliness.
Avoid Street Food
While tempting, street food in high-risk areas may not meet hygiene standards.
4. Maintain Clean Living Conditions
Dispose of Waste Properly
Proper disposal of human waste is critical in preventing the spread of amebiasis. This is especially important in communities without modern sewage systems.
Regular Cleaning
Disinfect surfaces in your home, particularly kitchen counters, sinks, and bathrooms.
5. Stay Informed While Traveling
Research High-Risk Areas
Understand the prevalence of amebiasis in your destination and take extra precautions when visiting such regions.
Pack Preventive Supplies
Carry hand sanitizers, disinfecting wipes, and water purification tablets for added safety.
Medications and Their Role in Prevention
While prevention through hygiene and sanitation is the first line of defense, certain medications can help manage and treat amebiasis. If diagnosed, doctors may prescribe medications like nizonide (nitazoxanide) as part of the treatment regimen. Here’s what you need to know:
What is Nizonide?
Nizonide contains nitazoxanide, an antiparasitic medication effective against a variety of protozoa, including Entamoeba histolytica. It works by interfering with the energy metabolism of the parasite, leading to its elimination. Nizonide is often used to treat intestinal infections caused by protozoa, making it a valuable tool in managing amebiasis.
When is Nizonide Used?
Active Infection
Nizonide is typically prescribed for confirmed cases of amebiasis to clear the infection.
Prophylactic Use
In some cases, doctors may recommend it for individuals who have been exposed to high-risk environments but have not yet shown symptoms.
How to Use Nizonide Effectively
Follow Dosage Instructions
Always take nizonide exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Complete the full course, even if symptoms improve early.
Combine with Other Treatments
Severe cases of amebiasis may require additional medications, such as metronidazole, to address systemic infections.
Monitor Side Effects
Common side effects include nausea, headache, or abdominal discomfort. Report any severe reactions to your healthcare provider.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Recognizing symptoms early and seeking medical advice is essential in managing amebiasis effectively. Delayed treatment can lead to complications such as liver abscesses, which are more challenging to treat. If you suspect an infection, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Public Health Measures
Preventing amebiasis on a larger scale involves improving public health infrastructure. Governments and organizations can play a pivotal role by:
Upgrading Sanitation Systems
Building modern sewage and waste disposal systems reduces the spread of parasites.
Providing Clean Water
Ensuring access to safe drinking water can significantly decrease infection rates.
Health Education Campaigns
Educating communities about hygiene practices and the risks of contaminated food and water can promote preventive behaviors.
Additional Tips for Vulnerable Groups
Certain populations, such as young children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals, are more vulnerable to amebiasis. Extra precautions for these groups include:
Avoiding High-Risk Foods
Stick to thoroughly cooked meals and avoid raw or unpeeled produce.
Frequent Health Checkups
Regular medical checkups can help detect infections early in at-risk individuals.
Vaccination Research
While no vaccine currently exists for amebiasis, ongoing research may offer preventive solutions in the future.
Conclusion
Preventing amebiasis requires a multifaceted approach, combining personal hygiene practices, safe food and water consumption, and access to medical care. Nizonide plays a crucial role in treating and managing infections, but the best defense remains proactive prevention. By staying informed, vigilant, and adopting these healthy habits, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting amebiasis and enjoy better overall health.
Whether at home or abroad, remember that small steps like handwashing and choosing safe drinking water can make a big difference. With collective efforts at both individual and community levels, the burden of amebiasis can be minimized, paving the way for healthier, safer living environments worldwide.











Post Comment