The Art of Heavy Machinery Welding: Ensuring Durability and Precision
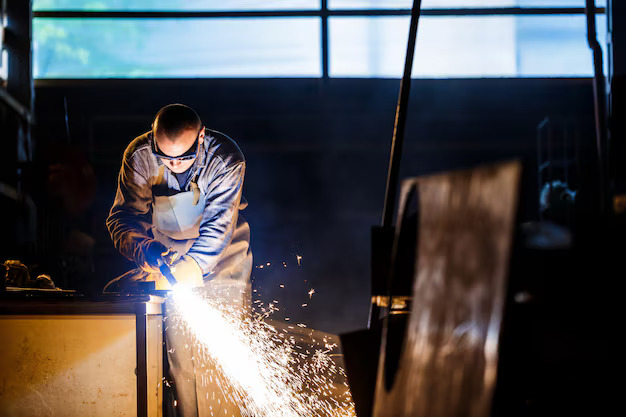
Crucially important in the manufacturing and maintenance sectors, heavy machinery welding guarantees that strong machines such as cranes, excavators, and bulldozers maintain integrity, strength, and operational lifetime. This intricate and expert procedure allows metal components to be precisely joined, therefore enabling machinery to operate at its best even under very demanding conditions. Heavy machinery welding is a cornerstone in maintaining the functionality of these machines, ensuring that they remain operational in the most challenging environments. Welding is crucial in maintaining large machinery working properly whether it comes to heavy construction, mining, or material handling. The demand for qualified welding experts has never been more critical since businesses depend on these machines for effective operations. Furthermore, underlined by the usage of heavy gear such as cardboard baling machines is the need for robust welding methods in guaranteeing their efficient operation.
The Science Supporting Heavy Machinery Welding
Welding large machinery goes beyond just connecting two metal components. It’s about knowing the mechanical characteristics of the materials being welded and how they will hold at the extreme pressures these machines run against. Welding is the study of heat, pressure, and chemical reactions to unite metals so producing a bond usually stronger than the base materials themselves.
Material Choice and Preparation: Making sure a weld is strong starts with selecting the correct materials. High-strength steels, alloys, and even specialized metals meant to resist great pressure and temperatures are among the common materials used in heavy machinery welding. To guarantee a neat and strong weld, the method begins with cleaning, grinding, or perhaps preheating these components.
Selecting the appropriate welding Method: Applications of many welding techniques— Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW), and Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) in heavy machinery The type of material, the component thickness, and the necessary joint strength all affect the proper approach. Because of their adaptability and performance on big, thick metal surfaces, techniques like SMAW and GMAW are usually favored for heavy machinery welding.
Precision and Accuracy: Precision is essential in heavy machinery welding to guarantee proper component alignment and strong welds all through the machine’s life. Welding not only combines metal but also guarantees that the construction maintains its durability, strength, and usefulness. Since even little misalignments can compromise the general functioning of the machine, special attention is required to guarantee that the welded components are not distorted.
The Difficulties with Heavy Machinery Welding
Large machine welding has various difficulties that must be addressed with the highest care and knowledge. One of the most difficult tasks is welding varying thicknesses of materials. The varied thickness of components including frames, hydraulic arms, and chassis calls for varied welding processes to provide strong and homogeneous joints.
- Thermal Strays and Warping: Welding generates a lot of heat that can produce thermal stresses in the material, warping or breaking results. In the case of large machinery, these problems could threaten the integrity and performance of important parts, therefore causing expensive repairs or downtime. To guarantee the final weld is strong and lasting, skilled welders must apply procedures to reduce heat distortion, including control of the speed and heat input during welding.
- Visibility and Access: Limited access to some parts of the machine makes welding big, heavy gear more difficult. Working in close quarters and near other components that can block their view or access to the region, welders sometimes have to Under these circumstances, one must be highly developed in welding abilities in addition to using specialized tools, equipment, and positioning systems.
- Environmental Elements: In demanding situations including factories, mining sites, and construction sites, where high temperatures, humidity, and even contact with corrosive compounds might compromise the integrity of the weld, heavy machinery is frequently used. For instance, whereas in humid situations welds may crack or weaken, in cold environments welding can produce brittle welds. Consequently, while planning and working, welders have to consider the surroundings.
Best Practices and Safety Welding
Safety is always first considering the great risk involved in heavy machinery welding. Working in tight areas, welders handling heavy machinery run several risks including heat exposure, welding fumes, electrical burns, and physical accidents. The integrity of the work being done as well as the welder’s safety depends on following the best standards and safety procedures.
- Shielding Gear: To guard themselves against burns, sparks, and dangerous UV radiation, welders have to don protective gear including flame-resistant gloves, jackets, helmets with face shields, and eye protection. Furthermore crucial is a welding fume extractor to avoid inhaling harmful vapors from widely used materials such as zinc, lead, and manganese, which are found in heavy equipment components.
- Learning and Development of Skills: Heavy machinery welding requires priority in training. Welders have to be not only adept in several welding methods but also knowledgeable about the machinery they are working on and how best to do repairs. Maintaining current with new technology and welding techniques guarantees that welders can satisfy the always-changing needs of the sector using constant learning.
- Inspection and Quality Control: Examining the welds for quality assurance is crucial once the welding operation is over. This covers X-ray imaging, ultrasonic testing, and visual examinations to find any internal flaws or imperfections likely to damage the strength and durability of the weld. Strong quality control measures guarantee the dependability and safe performance of the welded parts.
Final Thought: The Continual Function of Heavy Machinery Welding
One art form combining knowledge, ability, and accuracy is heavy machinery welding. It is essential for the machinery we depend on for building, mining, and material handling to be strong, safe, and durable. Every action, from the deliberate choice of materials to the welding method, has to be done precisely to guarantee a strong bond. Proper training, safety procedures, and quality control in place will help welders to keep creating strong, lifetime machines.
The value of heavy machinery welding will just keep rising as sectors change. Welding is still very essential even in the specialist field of material handling, where machines like cardboard baling machines depend on robust welds for their effective running. The capacity to produce strong and exact welds guarantees that any machine, for whatever its use, can operate consistently under pressure and in demanding environments.












Post Comment