Milling Machines: Essential Tools for Precision and Efficiency in Manufacturing
Milling machines are critical pieces of equipment in the world of manufacturing, playing a central role in the production of parts across a broad spectrum of industries. Whether it’s aerospace components, automotive parts, or consumer electronics, milling machines offer the precision and versatility needed for high-quality production. In this article, we’ll delve into what milling machines are, the different types of milling machines, their uses, and why they are indispensable in modern manufacturing.
What Are Milling Machines?
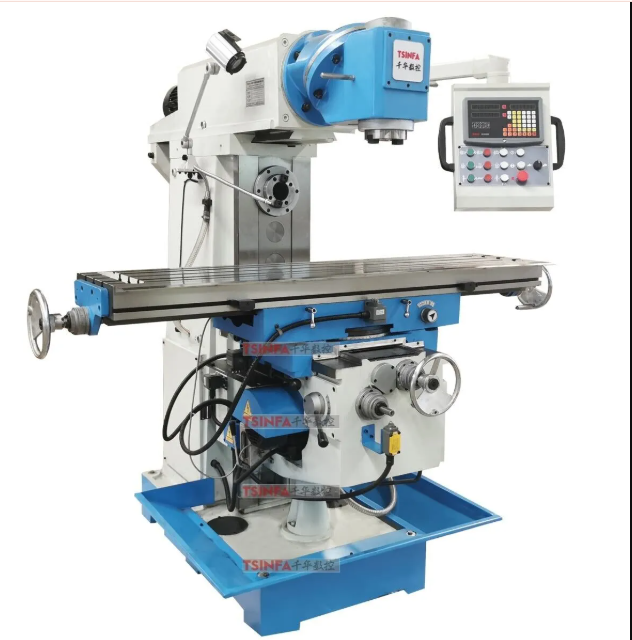
Milling machines are machining tools used for cutting, shaping, and drilling materials like metals, plastics, and composites. These machines employ a rotating cutting tool, typically called a milling cutter, which removes material from a stationary workpiece to achieve the desired shape or size. The process can be controlled manually or with computer-controlled systems like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) to enhance precision and automation.
Milling machines are highly versatile and capable of performing a wide range of operations, such as drilling, boring, engraving, and even gear cutting. Their ability to produce complex parts with high accuracy makes them indispensable in industries requiring precision manufacturing.
Types of Milling Machines
Milling machines come in a variety of forms, each designed for specific tasks. Below are some of the most common types of milling machines, each offering unique capabilities:
1. Vertical Milling Machines
Vertical milling machines have a vertically oriented spindle, which means that the cutting tool moves up and down while the workpiece remains stationary. The worktable can be moved in the X and Y axes, allowing the operator to position the part accurately under the tool.
Common Uses:
- Drilling, boring, and cutting tasks requiring high precision.
- Small parts and intricate shapes.
- Used in applications where a variety of cuts and geometries are needed.
Advantages:
- Ideal for operations involving smaller parts.
- Easier to set up and use for less complex tasks.
- Flexible for different operations, such as drilling and cutting.
2. Horizontal Milling Machines
Horizontal milling machines feature a horizontal spindle, and the cutting tool is mounted parallel to the worktable. The cutting tool moves along the horizontal plane to remove material from the workpiece. Horizontal machines are typically larger and more robust than vertical machines and are better suited for heavy-duty operations.
Common Uses:
- Heavy material removal, such as facing, slotting, and contour milling.
- Manufacturing large parts like engine blocks or large structural components.
- Ideal for long, flat parts with uniform thickness.
Advantages:
- More powerful and capable of handling heavy workloads.
- Excellent for producing large parts with complex features.
- More stable during heavy cuts, reducing the chances of vibrations.
3. CNC Milling Machines
CNC milling machines use computer programs to control the movement of the tool and the workpiece, offering a high degree of precision and automation. With CNC milling, the operator enters design specifications into the system, and the machine automatically performs the milling process with incredible accuracy.
Common Uses:
- High-precision parts with complex geometries.
- Mass production of identical components.
- Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing.
Advantages:
- Highly accurate, reducing human error.
- Can handle complex, detailed designs.
- Improved productivity with automated processes and minimal manual intervention.
4. Turret Milling Machines
Turret milling machines feature a fixed vertical spindle that can move in multiple directions, offering more flexibility in operations. The turret head can rotate and tilt, allowing for a wide range of cutting angles and orientations, making this type of machine ideal for versatile tasks.
Common Uses:
- Precision tasks requiring both vertical and horizontal movement.
- Suitable for small to medium-sized parts that require customization.
- Ideal for job shops or operations that require frequent changes in setups.
Advantages:
- Highly flexible, able to perform various tasks without major modifications.
- Efficient for both rough and finish machining.
- Convenient for shorter production runs and custom jobs.
5. Universal Milling Machines
Universal milling machines combine the features of both vertical and horizontal milling machines. These machines can operate in both orientations, allowing for greater flexibility in the types of milling processes they can perform.
Common Uses:
- Operations requiring both vertical and horizontal milling.
- Ideal for small-scale production or applications requiring multiple angles.
- Used in tool and die making, as well as custom part production.
Advantages:
- Extremely versatile for different types of machining.
- Allows for more flexibility in handling various workpiece configurations.
- Suitable for custom manufacturing and low-volume production.
Applications of Milling Machines
Milling machines are used across a wide range of industries for various applications. The precision and adaptability of these machines make them a go-to solution for producing high-quality parts with complex shapes.
1. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, milling machines are used to produce components that need to meet strict safety and quality standards. Parts like turbine blades, landing gear, and structural components require extreme precision and durability. CNC milling machines are particularly essential for manufacturing these complex parts efficiently and with tight tolerances.
2. Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry relies on milling machines for the production of a variety of parts, including engine components, transmission housings, and brake systems. Milling machines are used to produce high-strength parts that can withstand the stresses and strains found in automotive applications. The versatility of milling machines also allows for rapid prototyping and low-volume production of custom parts.
3. Medical Device Production
Milling machines are essential for producing medical devices, such as surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic equipment. The precision required for these parts is extremely high, and milling machines provide the accuracy needed to meet these rigorous standards. CNC milling allows for consistent, repeatable production of parts, making it ideal for the medical industry.
4. Consumer Electronics
Milling machines play a crucial role in the production of consumer electronics, where precision and fine details are necessary. Components like smartphone casings, laptop parts, and camera housings are often milled using advanced CNC machines. The ability to create complex, intricate designs and achieve fine tolerances makes milling machines essential for producing high-quality electronic devices.
5. Tool and Die Making
Milling machines are used extensively in tool and die making to produce molds, dies, and other tools used in manufacturing processes such as injection molding, die casting, and stamping. The precision of milling machines ensures that tools and dies meet exact specifications, allowing for the efficient and reliable production of parts across industries.
Advantages of Milling Machines
Milling machines offer several key benefits that make them indispensable in manufacturing:
1. High Precision and Accuracy
One of the primary advantages of milling machines is their ability to produce parts with high precision and accuracy. This makes them ideal for industries where even the smallest deviation in size or shape can result in product failure.
2. Versatility
Milling machines are versatile and can be used for a wide range of applications, from simple cuts to intricate and detailed designs. The ability to use different tools, such as drills, boring tools, and cutters, allows milling machines to handle multiple tasks on the same workpiece.
3. Complex Geometries
Milling machines, particularly CNC machines, excel at creating complex geometries that would be difficult to achieve with other machining processes. This makes milling ideal for parts with intricate features, such as aerospace components or medical devices.
4. Efficiency and Automation
With the advent of CNC milling, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of efficiency and automation. CNC machines can run continuously with minimal human intervention, improving productivity and reducing the risk of errors during production.
5. Customization
Milling machines are highly customizable, allowing operators to adapt machines for specific tasks or change settings quickly for different products. This flexibility makes milling machines suitable for both large-scale production and small-batch, custom manufacturing.
Conclusion
Milling machines are an essential part of modern manufacturing, offering the precision, versatility, and efficiency needed to produce high-quality parts across numerous industries. Whether used for mass production or custom manufacturing, milling machines enable the creation of complex components with tight tolerances and intricate designs. As technology continues to advance, milling machines will remain at the forefront of manufacturing innovation, driving the production of everything from everyday consumer products to high-tech aerospace components.











Post Comment