Advancing Bioinformatics Research in South Africa: The Role of Cutting-Edge Technologies
South Africa is becoming a hub for advanced biomedical research, with innovative technologies such as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), Bioinformatics, Proteomics, and Pharmacogenomics at the forefront of scientific discovery. These technologies are not only enhancing our understanding of genetics and diseases but are also paving the way for personalized medicine, a critical development in healthcare. In this post, we will explore how these technologies are revolutionizing the scientific landscape in South Africa.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): The Cornerstone of Molecular Biology
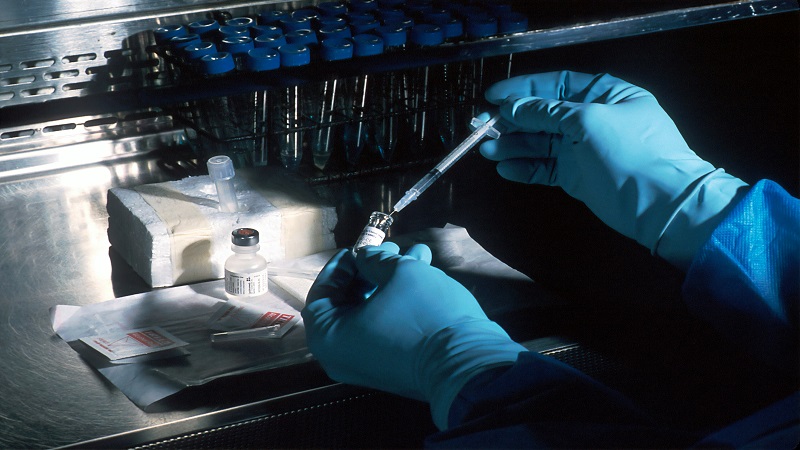
The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) has long been considered one of the most important tools in molecular biology. This technique makes it possible to increase the amount of a small segment of DNA to facilitate analysis as well as studies of genetic materials. Blacks in South Africa make extensive use of PCR in medical diagnoses, forensic science and also in research with a particular emphasis on the detection of infectious diseases like HIV and TB (tuberculosis). The fact that it is possible to amplify the DNA has made PCR an important technique for the diagnosis of genetic markers making the entire process even quicker and precise than before.
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS): Unlocking the Genome
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) has taken genetic research to new heights by allowing scientists to sequence entire genomes with unprecedented speed and accuracy. In South Africa, NGS technology is being used extensively in the investigation of some illnesses such as cancers, diabetes, and other genetic disorders. NGS technologies are actively utilized in various research institutes and hospitals, thus allowing doctors to do extensive genomic analysis and customize treatment options based on the patients.
With NGS, targeted therapy may be administered as the mechanisms of complex diseases are better understood at the genetic level. The South African genomics community has found use for this technology to great advantage as it has helped in understanding the genetic pool of various local populations, including those with unique genetic markers such as ethnic groups. This has its advantages by not only assisting in the control of the disease but also improving the development of localised therapies and precision medicine practice as a whole.
Bioinformatics: The Bridge Between Data and Discovery
To make sense of the massive amount of data provided by PCR and NGS, bioinformatics becomes crucial. Bioinformatics is the field of study that involves the use of computer applications for biological information, especially genetic data. In South Africa, bioinformatics is assisting researchers in understanding the complex gene-disease relations. The use of biological expertise with high-end computing, makes it possible to carry out data processing, modelling, and even simulation, effectively.
More and more research institutions and biotechnology companies in South Africa are using bioinformatics solutions for the evaluation of genomic and proteomic data. Such biomarker discovery and validation tools make it possible for scientists to assess disease risks, understand the course of the disease, and search for new ways of treatment. In addition, this field of study is very valuable in the process of drug development, where bioinformatics deals with the evaluation of how various drugs can work within the genetic framework of a patient so as to tailor the most effective regimen for that individual.
Proteomics: Understanding the Protein Landscape
Proteomics is the study of proteins and their activities on a large-scale level. Understanding their role is especially important for developing medical science because the majority of cellular functions are performed by proteins. In South Africa, growing evidence is shown on the application of proteomics in cancer, HIV and Alzheimer’s disease research. Exploring levels of the proteins and their relationship in the cell helps researchers in the identification of biomarkers to detect diseases at early stages and understand the pathology.
The adoption of proteomics technologies in South African laboratories is starting to result in some developments in tools for diagnosis and treatment. The emphasis on protein examination is also helping in the identification of drugable targets, from which new and better treatments can be designed.
Pharmacogenomics: Personalizing Medicine
Pharmoregulationgenomics is the domain that investigates the impact of gene variation on the response to drugs. Prescribing strategies for the given drug might be tailored to the individual patient’s genetic characteristics with such issues as drug metabolism, action, and efficacy addressed which is what pharmacogenomics does. In South Africa, the practice of pharmacogenomics is still in its infancy but is a promising area of research that seeks to address the challenges presented by the high burden of diseases in the country while minimizing adverse drug reactions and maximizing drug efficacy.
Additionally, pharmacogenomics is applicable to diseases characterized by wide inter-individual variability in drug responses, such as cancers, cardiovascular disorders, and psychiatric conditions. The practical utilization of pharmacogenomics in South Africa will thereby warrant the formulation of mammoth macromolecular treatment interventions that are personalized and adjusted for all patients to avoid administering strong medications with adverse effects.
The Future of Biomedical Research in South Africa
In South Africa, the prospects of carrying out biomedical research are quite good, propelled by ongoing technological developments. The application of PCR, NGS, Bioinformatics, Proteomics, and Pharmacogenomics is revolutionizing the healthcare system in South Africa as well as the whole continent. These advancements can help in new drug development, enhancing diagnostics, and facilitating better treatment options that are highly individualized, among other benefits.
The efforts made by South Africa in embracing these advanced technologies and encouraging innovation in the biomedical field shall ensure a healthier nation in the near future. It is expected that as these technologies develop and improve, so will the opportunities for South African scientists and health professionals to engage in contributing to knowledge and medical progress.
Conclusion
To sum up, the country of South Africa is utilizing sophisticated techniques such as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), Bioinformatics, Proteomics, and Pharmacogenomics in biomedical research and healthcare transformation. Given the developments taking place in these areas, it can be expected that South Africa will provide important breakthroughs in international medicine, offering a different perspective with regard to, among others, diseases and their management. The prospects for biomedical research in South Africa are extremely favourable, and these tools shall be the very foundation of the next phase of personalized medicine.
Also Read: Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Insurance Software












Post Comment